When it comes to building construction, the types of walls used play a crucial role in defining the overall structure’s strength, durability, and aesthetics. In this comprehensive post, we’ll delve into various types of walls commonly employed in construction projects.
Types of Walls
Table of Contents
From load-bearing walls to decorative partitions, understanding the characteristics and purposes of these walls will provide valuable insights for architects, builders, and anyone interested in the world of construction.
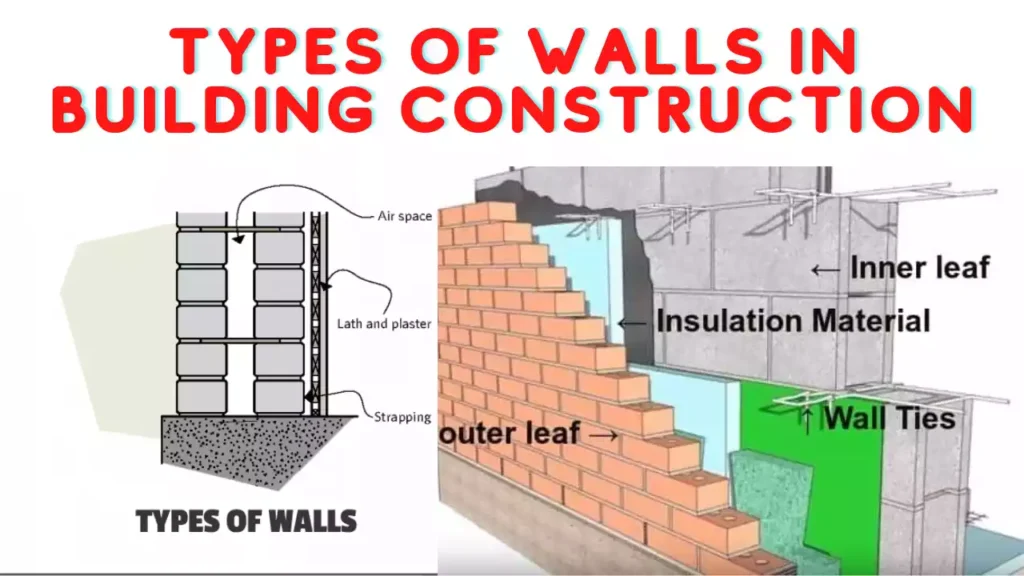
1. Load-Bearing Walls
Load-bearing walls are the backbone of any structure, responsible for carrying the weight of the building and transmitting it to the foundation. Typically constructed from materials like concrete, brick, or stone, these walls are strategically positioned to provide support and stability. It’s essential to ensure the proper design and construction of load-bearing walls to ensure the safety and longevity of the building.
2. Non-Load-Bearing Walls
Unlike load-bearing walls, non-load-bearing walls don’t bear the structural weight of the building. Instead, they serve as room dividers and enclosures. Gypsum board or timber-framed walls are often used for this purpose due to their versatility and ease of installation. These walls allow for flexible interior layouts and can be easily reconfigured to accommodate changing needs.
3. Curtain Walls
Curtain walls are exterior walls that do not support the building’s weight but rather act as a barrier against the elements. Typically made of lightweight materials such as glass, aluminum, or steel, curtain walls offer aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency. They allow for ample natural light and provide stunning views while maintaining the building’s insulation and weatherproofing.
4. Shear Walls
Shear walls are designed to resist lateral forces, such as those caused by wind or earthquakes. These walls are strategically placed throughout the structure to enhance its overall stability and prevent horizontal movement. Reinforced concrete is commonly used for shear walls due to its strength and durability.
5. Retaining Walls
Retaining walls are employed to hold back soil and create level surfaces on sloped terrains. They prevent erosion, manage water runoff, and provide functional spaces for landscaping. Retaining walls can be constructed from various materials, including concrete blocks, natural stone, and treated timber, offering both structural support and aesthetic appeal.
6. Partition Walls
Partition walls are interior walls that divide larger spaces into smaller rooms or areas. These walls contribute to the overall layout and organization of a building’s interior. Materials like gypsum board, hollow concrete blocks, or bricks are commonly used for partition walls due to their soundproofing and fire-resistant properties.
7. Hollow Walls
Hollow walls consist of two parallel layers with a hollow space in between. This design enhances insulation and reduces the transfer of sound between rooms. Hollow walls are often used in residential and commercial buildings to improve energy efficiency and create quieter indoor environments.
8. Load-Bearing Stone Walls
Load-bearing stone walls are a traditional construction method that utilizes natural stone, such as limestone or granite, to support the building’s weight. These walls showcase exceptional craftsmanship and provide a timeless aesthetic. While less common in modern construction, load-bearing stone walls continue to be used in restoration projects and heritage buildings.
9. Green Walls
Green walls, also known as living walls or vertical gardens, are a unique and eco-friendly approach to construction. These walls are adorned with vegetation that not only adds beauty but also improves air quality and insulation. Green walls can be installed both indoors and outdoors, creating a harmonious blend of architecture and nature.
10. Decorative Walls
Decorative walls serve primarily aesthetic purposes and can be found in various forms, including exposed brick walls, textured finishes, and artistic murals. These walls contribute to the overall visual appeal of a space and allow for creative expression. Decorative walls can be customized to match the desired ambiance and style of the building’s interior or exterior.
Recommended For You:
- Standard Window Size | 100+ Complete Standard Size of Window
- Concrete Mix Design | Concrete Mix Steps and Design Calculation
- Standard Car Parking Space Dimensions
Impact of Wall Material on Wall Types
Wall materials play a significant role in shaping the design, functionality, and aesthetics of a space. They come in a diverse range of options, each with its own set of characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks.
| Wall Material | Design Impact | Functionality Impact | Aesthetics Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brick | Timeless, rustic charm | Good insulation, thermal mass, durability | Textured, color variations, visual interest |
| Concrete | Industrial, minimalist aesthetics | Sturdiness, durability, thermal mass | Sleek/modern to raw aesthetics |
| Drywall | Versatile, easy to finish | Lightweight, easy installation | Clean, uniform, wide design possibilities |
| Wood Paneling | Warm, inviting ambiance | Some insulation, acoustic benefits | Natural texture, visual warmth |
| Stone | Luxury, authenticity | Durability, weather resistance, insulation | Timeless, grandeur, diverse aesthetics |
| Glass | Openness, transparency | Natural light, limited insulation | Spaciousness, contemporary, panoramic views |
Here’s an overview of some common wall materials and their impact on these aspects:
Brick:
- Design: Brick walls exude a timeless and rustic charm, suitable for both traditional and contemporary designs. They can be used for interior and exterior applications.
- Functionality: Bricks provide good insulation and thermal mass, helping to regulate indoor temperatures. They are durable and can withstand weather conditions.
- Aesthetics: The texture and color variations of bricks add visual interest and depth to a space. Exposed brick walls are often considered a desirable design feature.
Concrete:
- Design: Concrete walls can offer an industrial or minimalist aesthetic. They can be left exposed or finished in various ways, such as polished, stained, or textured.
- Functionality: Concrete is sturdy and durable, capable of withstanding significant wear and tear. It can provide good thermal mass and sound insulation.
- Aesthetics: Depending on the finish, concrete walls can appear sleek and modern or rugged and raw. They can be a focal point or a backdrop for other design elements.
Drywall (Gypsum Board):
- Design: Drywall is highly versatile and commonly used for interior walls. It can be easily painted, wallpapered, or textured to match various design styles.
- Functionality: Drywall is lightweight, easy to install, and provides a smooth surface for finishing. It doesn’t offer significant insulation on its own.
- Aesthetics: Drywall offers a clean and uniform look, allowing for a wide range of design possibilities through paint, textures, and decorative treatments.
Wood Paneling:
- Design: Wood panels provide a warm and inviting ambiance. They can create a cozy, traditional, or even contemporary atmosphere depending on the type of wood and the installation pattern.
- Functionality: Wood panels can add some insulation, but they might require additional measures to improve energy efficiency. They also offer acoustic benefits.
- Aesthetics: Wood paneling adds natural texture and visual warmth to a space. It can be stained, painted, or left natural, allowing for various aesthetic options.
Stone:
- Design: Stone walls exude a sense of luxury, elegance, and authenticity. They are often used as focal points in interior designs or as exterior cladding.
- Functionality: Stone offers excellent durability, weather resistance, and thermal mass. It can be a good insulator depending on its thickness.
- Aesthetics: The natural beauty of stone adds a sense of timelessness and grandeur. Different types of stone can create diverse aesthetics, from rustic to contemporary.
Glass:
- Design: Glass walls promote openness, transparency, and a seamless connection between indoor and outdoor spaces. They are commonly used in modern and minimalist designs.
- Functionality: Glass provides natural light, but it might lack privacy and insulation. Special coatings can enhance energy efficiency and UV protection.
- Aesthetics: Glass walls create a sense of spaciousness and can offer stunning views. They contribute to a sleek and contemporary aesthetic.
The choice of wall material greatly influences the overall look, feel, and functionality of a space. Designers and architects carefully consider these factors to create environments that align with their vision and the needs of the occupants.
Significance of Choosing Right Wall Types
Choosing the right wall types is of significant importance due to several key reasons:
- Structural Integrity: Different types of walls offer varying levels of structural stability and load-bearing capacity. The correct choice of wall type ensures that the building can safely support its own weight and the loads placed upon it.
- Insulation and Energy Efficiency: Certain wall materials provide better insulation properties, helping to regulate interior temperatures and reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling. Choosing walls with suitable insulation characteristics can lead to substantial energy savings over time.
- Soundproofing and Acoustics: The type of wall can greatly impact sound transmission between rooms and from the outside environment. Proper wall selection is crucial for maintaining privacy and creating acoustically comfortable spaces.
- Fire Resistance: Different wall materials possess varying degrees of fire resistance. Opting for fire-resistant walls, especially in areas prone to fires or for buildings with specific safety requirements, can help contain flames and protect occupants.
- Durability and Maintenance: Some wall types are more resistant to wear and tear, weathering, and deterioration over time. By choosing durable materials, maintenance costs and frequency can be reduced.
- Aesthetics and Design: Wall types contribute significantly to the visual appeal of a building’s interior and exterior. The right choice of materials can enhance the overall aesthetics, aligning with the desired architectural style and interior design.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental footprint of wall materials should be considered. Some options, like eco-friendly and sustainable materials, can reduce a building’s impact on the environment and promote sustainability.
- Cost Considerations: The initial cost of constructing walls varies based on the chosen materials. Additionally, ongoing maintenance, repair, and energy expenses can also be affected by the wall type. Balancing upfront costs with long-term benefits is essential.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Local building codes often dictate the minimum standards for wall construction, including fire safety, structural stability, and insulation requirements. Choosing the right wall types ensures compliance with these regulations.
- Functionality and Space Utilization: The intended use of the building and its specific spaces can influence the choice of wall materials. For example, flexible and movable walls might be more suitable for spaces that require frequent reconfiguration.
Significance of Wall Types in Architecture and Construction
Wall types hold immense significance in architecture and construction due to their multifaceted roles in shaping the overall functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability of buildings. Here’s a breakdown of their significance:
- Structural Support: Walls are fundamental load-bearing elements that provide stability to the entire structure. They resist vertical and lateral loads, ensuring the safety and longevity of the building.
- Space Division: Walls define the spatial layout of a building, creating rooms, corridors, and open areas. They contribute to the organization and flow of interior spaces, facilitating efficient use of the built environment.
- Environmental Control: Walls play a crucial role in regulating temperature, humidity, and acoustics within a building. They can provide thermal insulation, reduce noise transmission, and control natural light.
- Aesthetic Expression: Different wall materials, textures, and finishes contribute to the overall visual appeal of a building. The design of walls helps convey architectural style, personality, and character.
- Cultural and Historical Context: Wall types often carry cultural and historical significance. Traditional materials and construction techniques can be used to preserve cultural heritage and connect with local contexts.
- Sustainability: Wall materials and design impact a building’s energy efficiency and environmental performance. Properly designed walls with good insulation can reduce heating and cooling needs, leading to lower energy consumption.
- Adaptability: Walls can be designed for adaptability, allowing for future modifications or expansions without significant structural changes. This flexibility is essential for buildings that might need to evolve over time.
- Innovation and Technology: Advances in building technologies have led to innovative wall systems that incorporate features like smart insulation, self-cleaning surfaces, and integrated sustainable systems (solar panels, rainwater harvesting, etc.).
- Exterior Appearance: Walls contribute to a building’s curb appeal, creating a first impression on occupants and visitors. Different materials and design choices can help a building stand out or blend in with its surroundings.
- Resilience: In disaster-prone areas, walls can be designed to enhance a building’s resistance to earthquakes, hurricanes, and other natural disasters, thereby increasing its resilience.
- Occupant Well-Being: Interior walls influence occupants’ psychological well-being by providing privacy, visual comfort, and a sense of security.
- Cost Efficiency: The choice of wall materials and construction methods can impact the project’s budget. Well-considered choices can optimize cost while meeting performance requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions on Wall Types
What are the key factors to consider when choosing a wall type?
Choosing a wall type involves considering several factors, including structural requirements, desired aesthetics, functionality, budget, energy efficiency, and environmental impact. The purpose of the wall, its location within the building, climate conditions, and the availability of materials are also important considerations.
Are there any environmentally friendly wall materials?
Yes, several environmentally friendly wall materials are available. These include recycled materials like reclaimed wood and metal, natural materials like adobe and rammed earth, and sustainable options like bamboo. Additionally, materials with low embodied energy and those that promote energy efficiency, such as insulated concrete forms (ICFs) and structural insulated panels (SIPs), can also be considered eco-friendly choices.
How do load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls differ?
Load-bearing walls carry the weight of the building’s structure, transferring it to the foundation. They are essential for maintaining structural integrity. Non-load-bearing walls, on the other hand, don’t bear significant weight; they primarily define interior spaces and provide division without contributing to the building’s structural support.
Can non-load-bearing walls be removed or modified easily?
Yes, non-load-bearing walls can be removed or modified more easily than load-bearing walls. Since they don’t support the building’s structure, their removal or modification typically requires less engineering consideration. However, it’s important to consult a professional to ensure that the changes won’t impact the overall stability of the structure.
What are the benefits of using glass walls in interior design?
Glass walls offer a range of benefits in interior design, including creating a sense of openness, maximizing natural light, providing visual connectivity between spaces, enhancing aesthetics, and enabling efficient space utilization. They can also contribute to a modern and sophisticated ambiance.
How can I ensure proper insulation for exterior walls?
Proper insulation for exterior walls is crucial for energy efficiency. Choose appropriate insulation materials with the desired R-value (a measure of thermal resistance) for your climate. Consider options like insulated concrete forms (ICFs), structural insulated panels (SIPs), or traditional insulation materials like fiberglass or mineral wool. Proper installation and sealing are essential to prevent thermal leaks.
Are there regulations or permits needed for certain wall types?
Yes, regulations and permits can vary based on location and the type of wall construction. Load-bearing walls and major structural changes often require approval from local building authorities. Certain materials, especially those related to fire safety or environmental impact, might also be subject to regulations. It’s essential to consult with local authorities and professionals to ensure compliance with building codes and regulations.